Asymptote Of Tangent / Tangent Cotangent Secant And Cosecant Graphs Mathbitsnotebook A2 Ccss Math - So once again the zeroes of tangents and the x intercepts, integer multiples of pi.
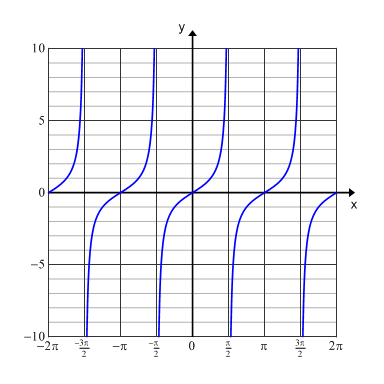
Asymptote Of Tangent / Tangent Cotangent Secant And Cosecant Graphs Mathbitsnotebook A2 Ccss Math - So once again the zeroes of tangents and the x intercepts, integer multiples of pi.. Finally, at the values of x at which tan x is undened, tan x has both left and right vertical asymptotes. There are many methods that can be used to determine the value for tangent such as referencing a table of tangents, using a calculator, and. Hence the equation of the normal at (2,8) is 12y + x = 98. As you can see, the tangent has a period of π, with each period separated by a vertical asymptote. Is that asymptote is (analysis) a straight line which a curve approaches arbitrarily closely, as they go to infinity the limit of the curve, its tangent at infinity while tangent is (geometry) a straight line touching a curve at a single point without.
When a linear asymptote is not horizontal or vertical, it is called. Hence the equation of the normal at (2,8) is 12y + x = 98. Let's put dots for the zeroes and dashed vertical lines now we can use what we know about sine, cosine, and asymptotes to fill in the rest of the tangent's graph: The function tan x is dened for all real numbers x such that cos x = 0, since tangent is the quotient of sine over cosine. It would be nice if it could work also from the hyperbola center to have a more 'geometrical' and easy way to draw the asymptotes of a hyperbola (instead of using.
Or an odd integer times 1/2).
Let's put dots for the zeroes and dashed vertical lines now we can use what we know about sine, cosine, and asymptotes to fill in the rest of the tangent's graph: Tangent line a line tangent to a curve is one that only touches the curve at only one point. Dummies has always stood for taking on complex concepts and making them easy to understand. Algebraic method in finding the asymptote of a curve. An asymptote can occur when a denominator in a function includes a vertical asymptotes are vertical lines near which the function grows to infinity. Therefore, to find the intercepts, find when sin(theta)=0. An asymptote is a line that the graph of a function approaches, but never intersects. Specically, if a is a value of x outside the domain of tan x, then. The lesson here demonstrates how to determine where on a graph the asymptotes for tangent and cotangent functions will occur. Whether it's to pass that big test, qualify for that big promotion or even master that cooking technique; Graphs of tangent and cotangent functions ppt video online download. The curve can approach from any side (such as from above or below for a horizontal asymptote), or may actually cross over (possibly many times), and even move away and back again. In terms of right triangles and in terms of the unit circle.
Graph trig functions sine cosine and tangent with all of the transformations in this set of videos we see how the. How do i find the period of a function? Asymptotes can be vertical, oblique (slant) and horizontal. Recall that #tan# has an identity: To graph a tangent function, we first determine the period (the distance/time for a complete oscillation), the.
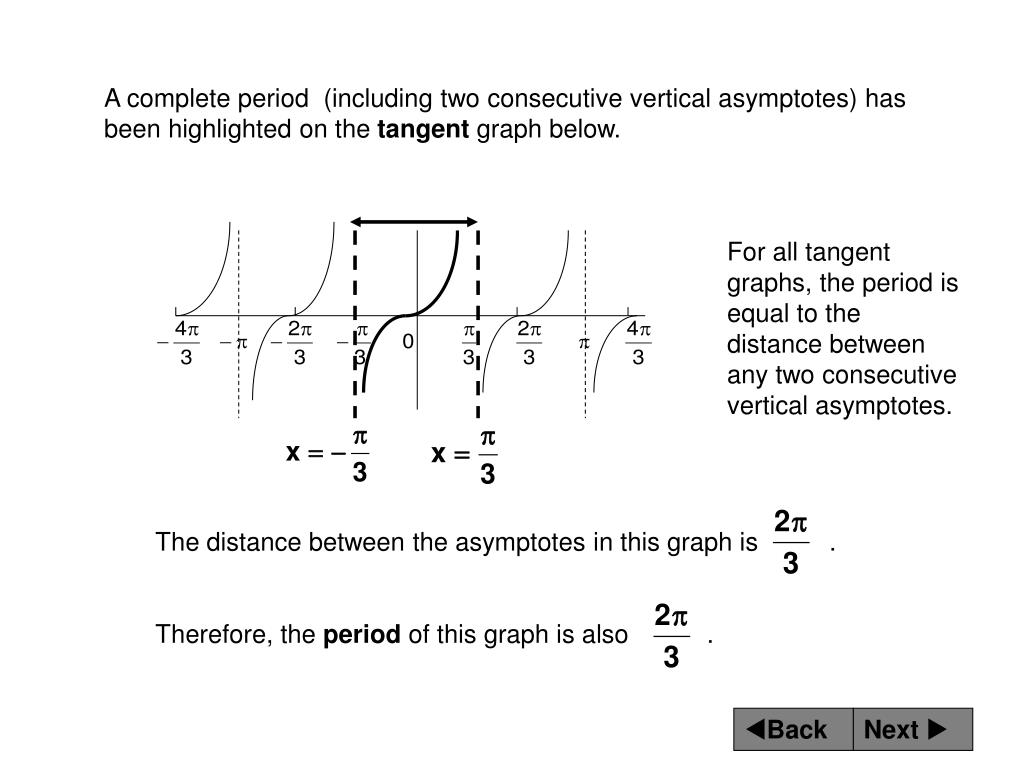
Definition of the tangent function and exploration of the graph of the general tangent function and its properties such as period and asymptotes are presented.
Algebraic method in finding the asymptote of a curve. As nouns the difference between asymptote and tangent. To graph a tangent function, we first determine the period (the distance/time for a complete oscillation), the. Tangent line a line tangent to a curve is one that only touches the curve at only one point. Tool to find the equations of the asymptotes (horizontal, vertical, oblique) of a function. In terms of right triangles and in terms of the unit circle. An explanation of how to find vertical asymptotes for trig functions along with an example of finding them for tangent functions. Graphs of tangent and cotangent functions ppt video online download. The concept of amplitude doesn't really apply. Let a plane curve be defined by the parametric equations. A horizontal asymptote is often considered as a special case of an oblique asymptote. Whether it's to pass that big test, qualify for that big promotion or even master that cooking technique; See all area asymptotes critical points derivative domain eigenvalues eigenvectors expand extreme points factor implicit derivative inflection points intercepts inverse laplace inverse laplace.
Or an odd integer times 1/2). Therefore, to find the intercepts, find when sin(theta)=0. 5 tutorials that teach finding the asymptotes of tangent and cotangent. The slope of the curve definitely approaches zero as $x$ approaches the asymptotic approach is not considered a form of tangency. You'll have the same graph than tan, but instead of having the asymptotes separated on intervals of pi, you have them every pi/2 and instead of starting at pi/2, you start at 0.

Graph trig functions sine cosine and tangent with all of the transformations in this set of videos we see how the.
The slope of the curve definitely approaches zero as $x$ approaches the asymptotic approach is not considered a form of tangency. How do i find the period of a function? #theta=pi/2+n pi, n in zz#. In terms of right triangles and in terms of the unit circle. The lesson here demonstrates how to determine where on a graph the asymptotes for tangent and cotangent functions will occur. To find the vertical asymptotes. A horizontal asymptote is often considered as a special case of an oblique asymptote. In analytic geometry, an asymptote (/ˈæsɪmptoʊt/) of a curve is a line such that the distance between the curve and the line approaches zero as one or both of the x or y coordinates tends to infinity. Use the basic period for. The concept of amplitude doesn't really apply. The asymptotes are lines that tend (similar to a tangent) to function dcode retains ownership of the online 'asymptote of a function' tool source code. There are two main ways in which trigonometric functions are typically discussed: As you can see, the tangent has a period of π, with each period separated by a vertical asymptote.